1.Swagger
Swagger 给我们提供了一个全新的维护 API 文档的方式,可以很好地降低前端开发人员与后端开发人员对WebAPI接口的沟通成本。它可以动态生成Api接口文档,促进项目高效开发。下面我们就来了解一下它的优点:
- 代码变,文档变。只需要少量的注解,Swagger 就可以根据代码自动生成 API 文档,很好的保证了文档的时效性。
- 跨语言性,支持 40 多种语言。
- Swagger UI 呈现出来的是一份可交互式的 API 文档,我们可以直接在文档页面尝试 API 的调用,省去了准备复杂的调用参数的过程。
- 还可以将文档规范导入相关的工具(例如 SoapUI), 这些工具将会为我们自动地创建自动化测试。
在项目中常用的注解说明和案例
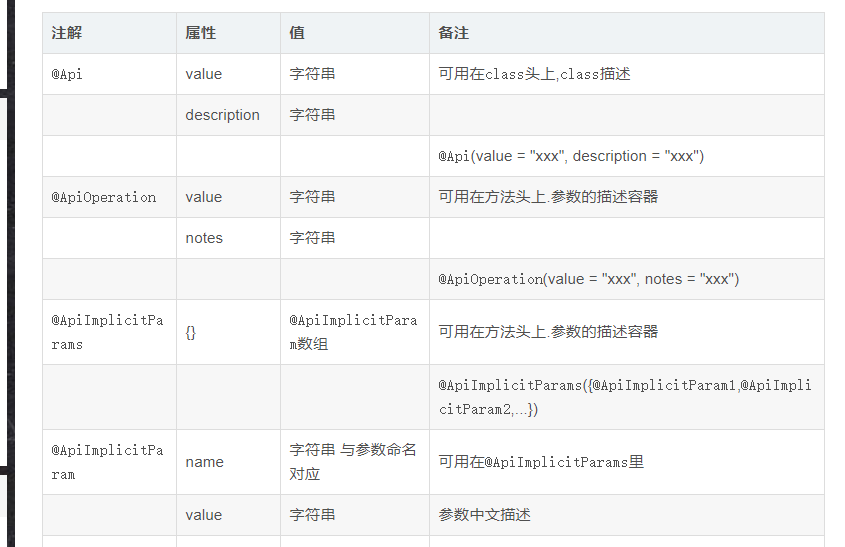
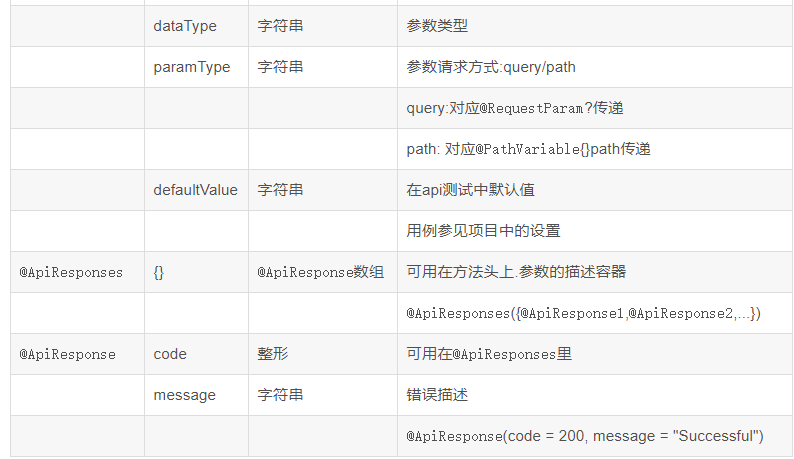
下面我们来创建一个Spring Boot项目测试一下。
2.工程创建
首先是创建一个Spring Boot项目,创建成功后,加入web依赖,加入两个Swagger2相关的依赖,完整的依赖如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
2.1Swagger2配置
在项目创建成功之后,只需要创建一个配置类提供一个Docket的Bean即可,如下:
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Config {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.pathMapping("/")
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example.swagger2.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build().apiInfo(new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("SpringBoot整合Swagger")
.description("接口文档描述信息......")
.version("1.0")
.contact(new Contact("涛声依旧","https://blog.csdn.net/ourstronger","aaa@gmail.com"))
.license("The Apache License")
.licenseUrl("http://www.baidu.com")
.build());
}
}
|
@EnableSwagger2注解启用Swagger2 .
这个Bean中,配置映射路径和要扫描的接口的位置,在apiInfo中,主要配置一下Swagger2文档网站的信息,例如网站的title,网站的描述,联系人的信息,使用的协议等等。
配置完后,Swagger2就算配置成功了。
此时启动项目,输入http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html,能够看到如下页面,说明已经配置成功了:
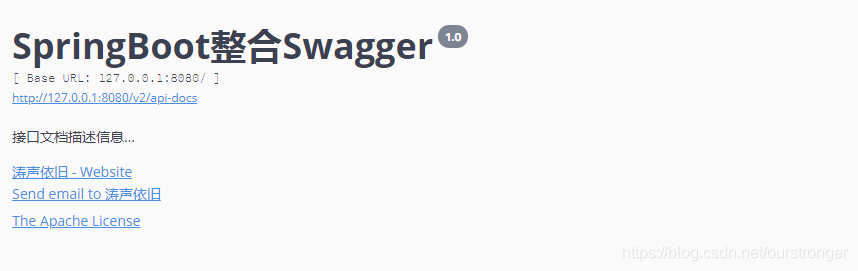
2.2.创建接口
Swagger2相关的注解其实并不多,上文中已经列出来了,下来创建一个增删改查举例说明:
@RestController
@Api(tags = "用户数据接口")
public class UserController {
@ApiOperation(value = "查询用户",notes = "根据id查询用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name= "id",value = "用户id",required = true,defaultValue = "66")
@GetMapping("/user")
public User getUserById(Integer id){
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
return user;
}
@ApiOperation(value = "删除用户",notes = "根据id删")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id",value = "用户id",required = true,defaultValue = "55")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code = 200,message = "删除成功"),
@ApiResponse(code = 500,message = "失败")
})
@DeleteMapping("/user/{id}")
public void deleteUserById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("deleteUserById:"+id);
}
@PostMapping("/user")
@ApiOperation(value = "添加用户",notes = "添加用户接口")
public User addUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return user;
}
@PutMapping("/user")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name="id",value = "用户id",required = true,defaultValue = "77"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="username",value = "用户名",required = true,defaultValue = "taoge"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name="address",value = "地址",required = true,defaultValue = "深圳")
})
@ApiOperation(value = "更新用户",notes= "根据id更新用户的接口")
public User updateUserById(@RequestBody User user) {
return user;
}
}
|
@ApiIgnore 注解:如果想在文档中屏蔽掉删除用户的接口(user/delete),那么只需要在删除用户的方法上加上 @ApiIgnore 即可。
如果参数是一个对象(例如上文的更新接口),对于参数的描述也可以放在实体类中。例如下面一段代码:
@ApiModel
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户id")
private Integer id;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户名")
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户地址")
private String address;
}
|
经过如上配置之后,接下来,刷新刚刚打开的页面,可以看到如下效果:
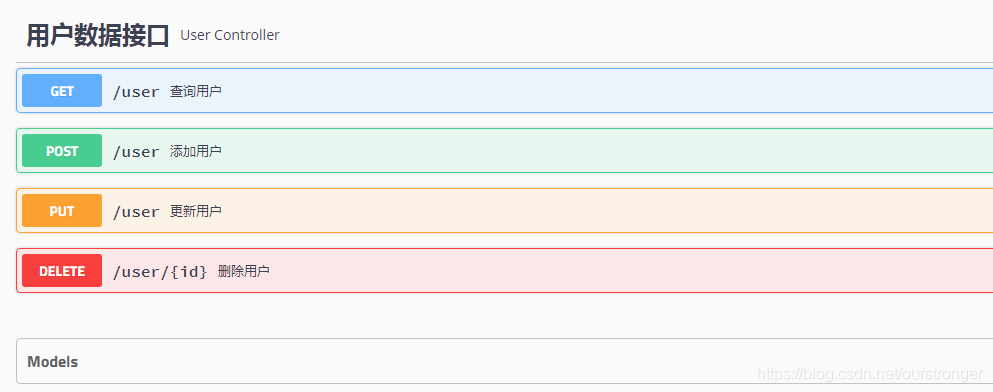
可以看到,所有的接口这里都列出来了,包括接口请求方式,接口地址以及接口的名字等,点开一个接口,可以看到如下信息:
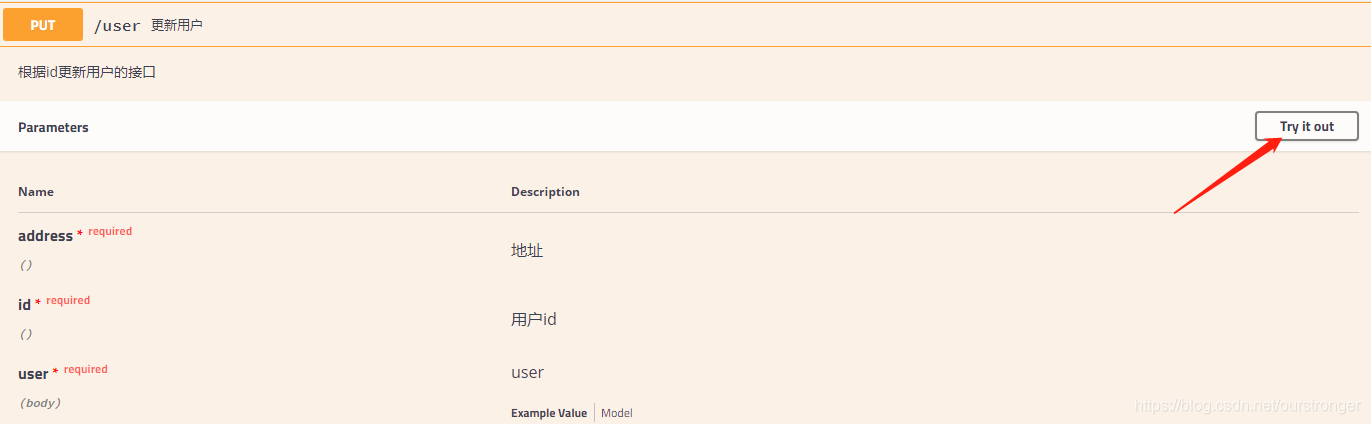
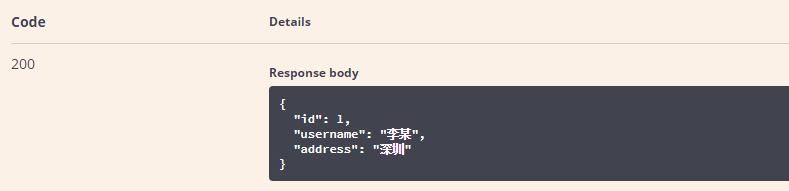
参数类型下的query表示参数以key/value的形式传递,点击右上角的Try it out,就可以进行接口测试:
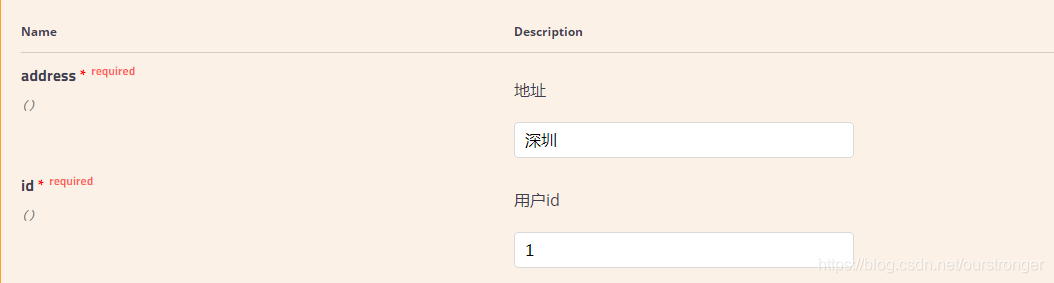
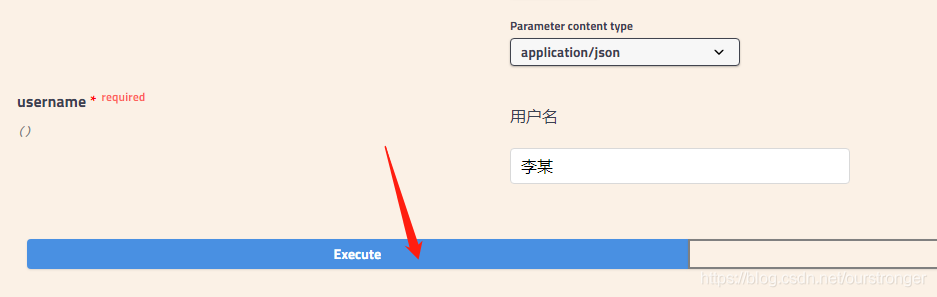
点击Execute按钮,表示发送请求进行测试。测试结果会展示在下面的Response中。
2.3.在Security中的配置
如果我们的Spring Boot项目中集成了Spring Security,那么如果不做额外配置,Swagger2文档可能会被拦截,此时只需要在Spring Security的配置类中重写configure方法,添加如下过滤即可:
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/swagger-ui.html")
.antMatchers("/v2/**")
.antMatchers("/swagger-resources/**");
}
|
如此之后,Swagger2文件就不需要认证就能访问了。
项目已上传至github,具体请下载示例代码测试:https://github.com/astronger/springboot-swagger2